Conditions
Our vision is to provide convenient access to current health information and education for all patients, consumer and members of community on urology and prevention of diseases. We have divided this patient and consumer information into different sections below so as to help you navigate easier. Some of the sections are again divided for better navigation within the website.
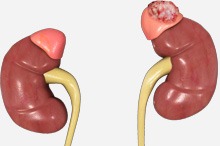
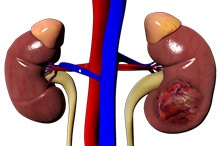
Adrenal Tumours
The adrenal glands, situated above each kidney, are endocrine glands that secrete hormones into the blood to regulate metabolism and various sexual functions, and respond to emergency situations. Each gland is made up of an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Tumours in the adrenal gland are rare and usually benign, but may also be malignant. They are caused by an inherited faulty gene.
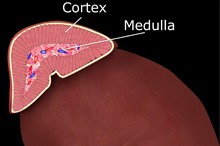
Adrenal Condition
Adrenal glands are small glands which are triangular in shape and located on top of each kidney. These glands consist of two parts: the adrenal cortex (outer region) and the adrenal medulla (inner region). The function of the adrenal glands is to produce hormones including cortisol (responds to stress and helps regulate blood sugar, blood pressure (BP), immunity, metabolism, bone and nervous system),
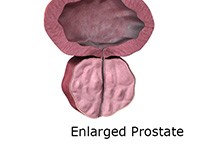
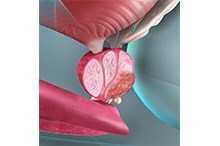
Benign Prostatic Enlargement
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or benign prostatic hypertrophy is enlargement of the prostate gland. The word "benign" means the cells are not cancerous. "Hyperplasia" refers to an increased number of cells.
Bladder cancer
Bladder cancer is responsible for approximately 3% of all malignancies diagnosed in Australia each year. It is more common in men than women and typically affects those over 60 years of age.
Cystic Disease
A cyst is a sac filled with fluid or semisolid material, which may appear anywhere in the body. Cystic disease refers to the development of cysts on the kidney.
Elevated PSA
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein produced by cells of the prostate gland. It is normal for men to have a low level of PSA in their blood. However, prostate cancer or benign (non-cancerous) conditions can increase the PSA level.
Haematuria
Haematuria is a common condition and one which must be taken seriously. Haematuria simply means blood in urine. If you notice blood in the urine it should always be investigated, although in most cases no serious cause will be found.
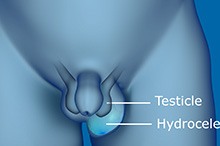
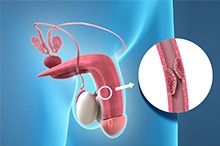
Hydrocele/Spermatocele
A hydrocele is an accumulation of fluid around the testicles causing the scrotum to swell. This is caused due to non-closure of the tube through which the testicles descend into scrotum. Non-closure of the tube leads to accumulation of fluid in the scrotum. Inflammation or injury of the testicles, or blockage within the spermatic cord by fluid or blood may also cause hydrocele.
Hydronephrosis
Hydronephrosis is a condition in which one or both kidneys become swollen due to failure of the urine to drain from the kidney(s) to the bladder. This can occur due to either blockage or backflow of urine.
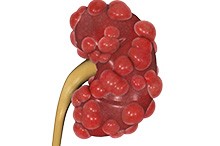
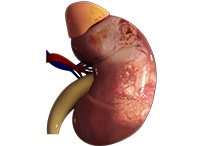
Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer or renal cancer is a malignant disease of the kidney cells. Renal cell carcinoma affects the tubules of the kidneys and is the most common form of kidney cancer in adults. Sometimes young children develop a form of kidney cancer called Wilms’ tumour. Men are more predisposed to the condition than women, mainly occurring between the ages of 50 to 70.
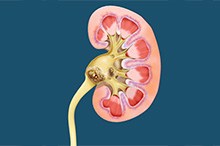
Kidney Cysts
Cysts are abnormal fluid or semisolid-filled sacs that may arise in any tissue of the body, including the kidneys. They may be associated with serious conditions where they present as multiple cysts affecting kidney function, but are usually seen as simple single cysts that are noncancerous. Simple cysts are more common in men and usually develop with age.
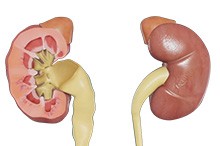
Kidney Stones
As the kidneys filter blood of impurities, minerals and acid salts can accumulate and harden over time. These solid crystalline deposits are called kidney stones, and can form in one or both kidneys. The stones can travel down the urinary tract and block the flow of urine, causing pain and bleeding.
Nocturia
Nocturia is a condition where you feel the need to urinate often in the night. This may be a part of the normal ageing process, an underlying medical condition or simply drinking too much water.
Pheochromocytoma
Pheochromocytoma is a rare non-malignant tumour of the adrenal gland that secretes high levels of epinephrine and nor epinephrine which may cause an increase in blood pressure, heart rate and metabolism. If unrecognised and untreated it may cause life threatening consequences. The condition may develop at any age, but is more common in middle age.
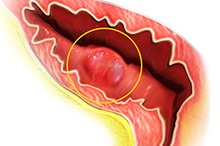
Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancers found in men where abnormal cells grow out of control in the prostate gland. It may be confined within the gland or may be aggressive and spread to other parts of the body and cause serious complications. Therefore, screening for prostate cancer at earlier stages is always beneficial so that effective treatment can be provided.
Transitional Cell Cancer
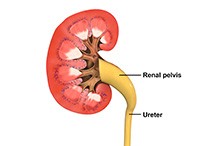
Your kidneys filter blood to produce urine, which is carried by tubes called ureters to the bladder. The junction between a kidney and ureter forms a funnel-shaped renal pelvis. Transitional cells are specialised cells that line the renal pelvis and ureters, and have the ability to stretch without damage.
Urethral Cancer
Urine stored in the bladder passes outside the body through a tube called the urethra. It is a short tube that passes through the vagina in women, but is longer in men, running through the penis. Urethral cancer is a rare form of cancer that affects the cells and glands lining the urethra. It is more common in women, over the age of 60.
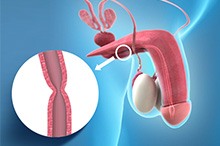
Urethral Strictures
The urethra is a tube through which urine, stored in the bladder, is passed outside the body. A urethral stricture is an abnormal area of constriction along the length of the urethra that reduces or obstructs the flow of urine. It is more common in males as the urethra is longer, passing through the penis and prostate gland.
Urological Oncology (Cancer)
Cancer is a disease that results from abnormal growth and division of cells that make up the body's tissues and organs. Under normal circumstances, cells reproduce in an orderly fashion to replace old cells, maintain tissue health and repair injuries. However,
Varicoceles
Varicoceles are abnormal enlargements of the veins in the scrotum. It is commonly found in adolescent boys in puberty, and occurs mostly around the left testicle, but can also occur on both sides. Varicocele is generally harmless and doesn’t cause any pain, however; some boys may complain of heaviness in the scrotum,
Urinary Reflux (Vesicoureteral Reflux)
Urine is formed in the kidneys, flows down through thin tubes called ureters, and is temporarily stored in the bladder before being excreted to the outside. The valves in the ureters, muscles of the ureters and bladder, and the pressure created by urine in the bladder, ensure this unidirectional flow. Vesicoureteral reflux, a condition commonly diagnosed in infants and children,
Von Hippel-Lindau Disease
Von Hippel-Lindau disease (VHL) is an inherited genetic disorder characterised by benign and cancerous tumours in parts of the body that have a rich supply of blood vessels. It is a rare condition that develops from the abnormal growth of blood vessels as knots (hemangioblastomas) in the brain,

 Menu
Menu